What is Polystyrene
- Postdate: 2023-05-09
- From: qibochem.com
-
What is Polystyrene
- Postdate: 2023-05-09
- Form: qibochem.com
-
Introduction:
Polystyrene (Polystyrene, abbreviated as PS) refers to a polymer synthesized by free radical addition polymerization of styrene monomer, and its chemical formula is (C8H8)n. It is a colorless and transparent thermoplastic with a glass transition temperature higher than 100°C, so it is often used to make various disposable containers that need to withstand the temperature of boiling water, as well as disposable foam lunch boxes.
The glass transition temperature of polystyrene is 80-105°C, the amorphous density is 1.04-1.06g/cm3, the crystal density is 1.11-1.12g/cm3, the melting temperature is 240°C, and the resistivity is 1020-1022Ω·cm. The thermal conductivity is 0.116 W/(m Kelvin) at 30°C. Ordinary polystyrene is an amorphous random polymer with excellent heat insulation, insulation and transparency. The long-term use temperature is 0-70°C, but it is brittle and easy to crack at low temperature. There are also isotactic and syndiotactic as well as atactic polystyrene. Isotactic polymers are highly crystalline, and syndiotactic polymers are partially crystalline.
Classification:
Polystyrene (PS) includes ordinary polystyrene, expanded polystyrene (EPS), high impact polystyrene (HIPS) and syndiotactic polystyrene (SPS). Ordinary polystyrene resin is non-toxic, odorless, colorless transparent particles, glass-like brittle materials, its products have extremely high transparency, light transmittance can reach more than 90%, good electrical insulation performance, easy to color, process Good fluidity, good rigidity and good chemical corrosion resistance. The disadvantages of ordinary polystyrene are brittleness, low impact strength, prone to stress cracking, poor heat resistance and intolerance to boiling water.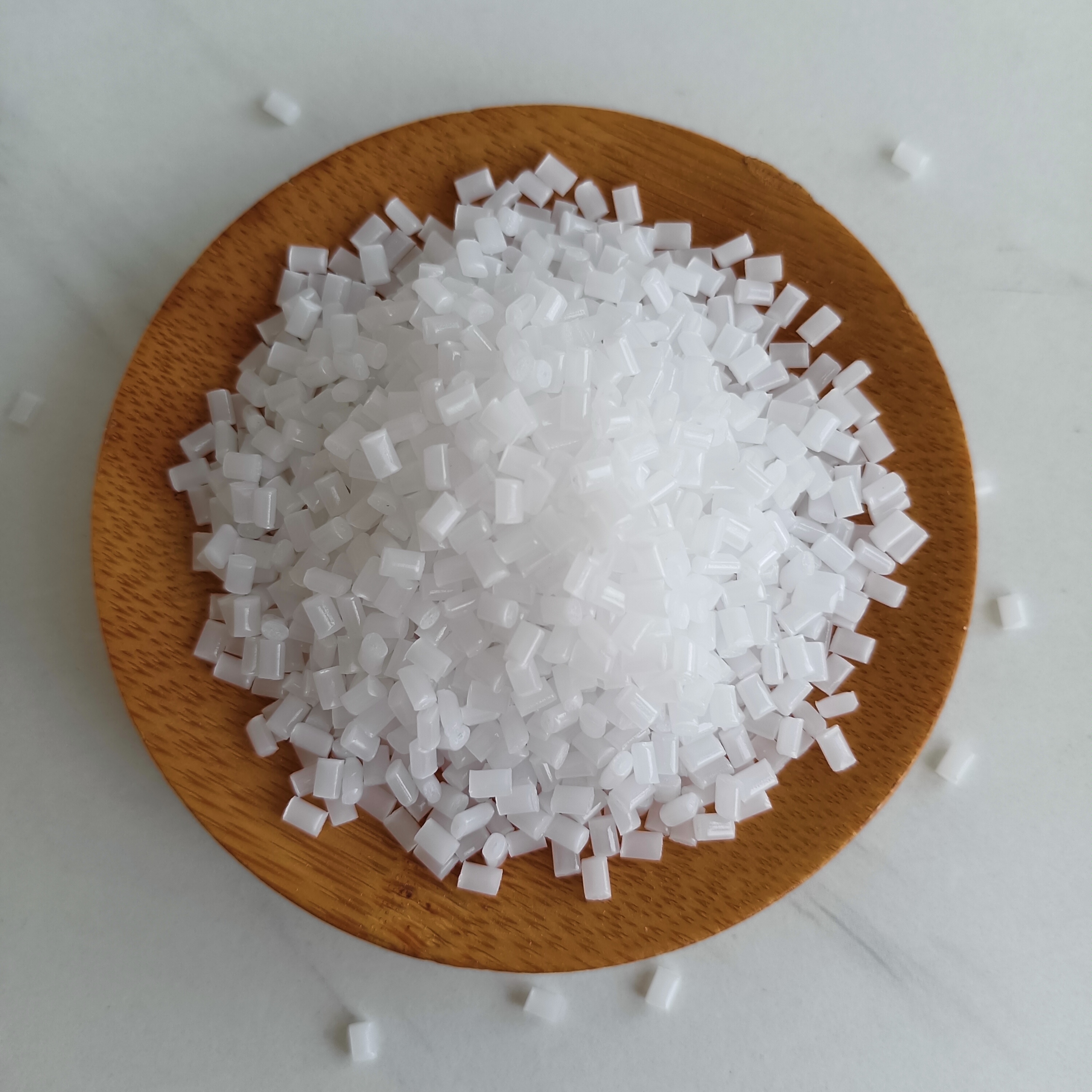
Attributes:
Ordinary polystyrene resin is an amorphous polymer. The side groups of polystyrene macromolecular chains are benzene rings, and the random arrangement of bulky side groups is benzene rings, which determines the physical and chemical properties of polystyrene, such as high transparency. , high rigidity, high glass transition temperature, brittle and so on. Expandable polystyrene is made by impregnating low-boiling point physical blowing agent in ordinary polystyrene, and it is heated and foamed during processing, and is specially used for making foam plastic products. High-impact polystyrene is a copolymer of styrene and butadiene, butadiene is the dispersed phase, which improves the impact strength of the material, but the product is opaque. Syndiotactic polystyrene has a syndiotactic structure and is produced by metallocene catalysts. It is a new polystyrene variety with good performance and belongs to engineering plastics.
Application:
Polystyrene is easy to process and shape, and has the advantages of transparency, cheapness, rigidity, insulation, and good printability. It can be widely used in light industry market, daily decoration, lighting instructions and packaging, etc. In terms of electricity, it is a good insulating material and thermal insulation material. It can be used to make various instrument casings, lampshades, optical and chemical instrument parts, transparent films, capacitor dielectric layers, etc.
It can also be used in powder and emulsion cosmetics. Because the powder cake has good compressibility, it can improve the adhesion performance of the powder. It is an advanced filler that replaces talc and silica to give skin luster and lubricity.
Shijiazhuang Qibo Chemical Co., Ltd. has developed a new type of high-efficiency reactive flame retardant - halogen-free PS flame retardant.The addition ratio is 4% (the maximum addition ratio is 5%); one is suitable for halogen-free PS flame retardant, and the other is suitable for halogen-free transparent PS flame retardant. P (phosphorus) element is synthesized by N (nitrogen) in a reactor, and then prepared through a composite process.
The flame-retardant PS prepared by this product meets the halogen-free requirements of the International Electrotechnical Association IEC 61249-2-21:2003, IEC 61249-2-21 and other standards.